Our LEAN glossary gives you a definition of words and terminologies often used
Toyota defined three concepts of eliminating waste; Muda, Muri and Mura.
5S stands for five different focus areas to ensure optimal flow.
5S – You are already doing it >
Seiri
Translates to sorting.
Remove items not relevant for the work or location. Reduce time looking for items. Reduce distraction due to mess. Optimize use of available space.
Seiton
Translates to set in order or straighten.
Create an optimal workflow by placing items where they are applicable. Keep tools and appliances near the task at hand.
Seido
Translates to shine.
Keep your workplace clean and tidy. Inspect and shine regularly to keep a pleasing workplace. Defects are detected more easily; waste and errors are reduced.
Seiketsu
Translates to standardize.
Ensure repetition of the first three S’s. This is where the practice is established, supported by processes and procedures.
Shitsuke
Translates to sustain self-discipline.
When the practice is established, a culture is developed where people are self-motivated to continue and improve the new practice. The employees have taken ownership of the process.
This is a technique to understand the underlying causes to a problem. The concept is to ask “WHY?” for each described symptom until you have gone beyond the surface and aim for the root cause.
The technique does not dictate asking “why” only 5 times. Use it more or less according to the depth of the problem.
This defines 8 areas of wastes helping lean agents and organizations to eliminate waste in their work processes.
The A3 method is typically used for structured problem-solving. Based on the A3 paper format, Toyota forced their employees to narrow down their input to the cure of the business. The A3 format couldn’t fit everything, so the communication had to be effective.
The principle is that the A3 consist of multiple sections guiding the users through steps to define the problem, the desired state, and to identify their path going forward.
Typical fields for a problem-solving A3 are:
The A3 is a living document being used, reviewed, adjusted according to the PDCA cycle until the desired state has been achieved.
The A3 method is also suitable for other use, such as a business canvas etc.
Add autonomy and authority to the workers to notify management and also stop production in case of quality issues. Andon is part of the Jidoka method.
The meaning of andon is light a lantern. The background is to stop and warn everyone that there is a problem and production is stopped.
Using andon requires autonomy and management trusting their employees. The workers must be competent and not be subjected to reprimand.
A principle of designing the tools, manufacturing equipment and processes, so errors cannot be made; idiot-proofing or fool-proofing.
A bottleneck is somewhere in your process that can’t keep up with the pace of the rest, causing a pile-up. It disturbs or prevents flow, a prerequisite for effective processes, and affects your takt time.
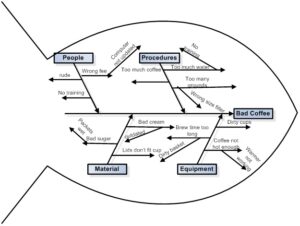
Created by Kaoru Ishikawa, the diagram is originally named “Ishikawa diagram”, but more commonly referred to as the fishbone diagram.
The diagram is used to visualize cause and effect of causal events that led to the problem.
Flow is all about optimizing the processes to deliver products evenly and steadily with the right quality. All sections of the process must be aligned with each other to avoid a pile-up or waiting time (waste).
The concept is about moving one item at the time through the process (pull) instead of stocking up for delivery (push).
Translates to “actual place”. Typically, where the production is being done.
Gemba is therefore a place, and not an action. We often refer to a “Gemba walk” as something we do, but it’s more accurate to say “Go to Gemba” – go to the actual place.
Genchi Genbutsu is pretty much the same as Gemba. Genchi Genbutsu can translate to the actual machine and actual product. The principles are shared with Gemba – go see the problem where it actually happens.
Some mean that there are differences in the meaning and mindset of Gemba and Genchi Genbutsu; Where Gemba is about solving and fixing problems and Genchi Genbutsu is more to identify and look for improvement opportunities.
Translates to realness. It quantifies the problem through observed data required to understand the problem.
Genjitsu is normally achieved during Gemba and Genbutsu.
Translates to self-reflection and is strongly related to Kaizen and continuous improvement.
Avoid mistakes or repeating mistakes by identifying issues along the way and plan to prevent issues going forward.
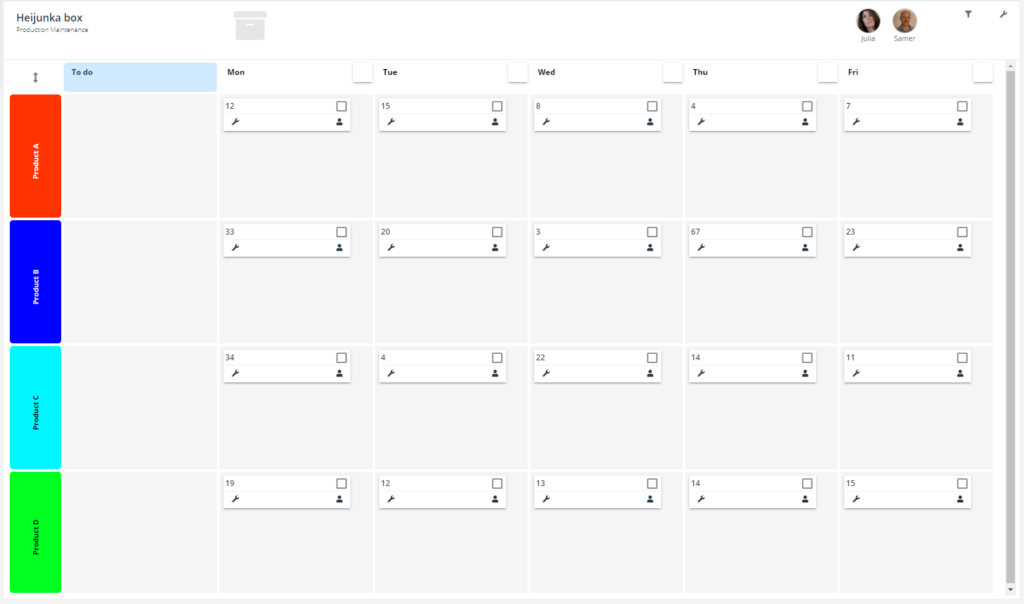
Heijunka is the concept of leveling the production to meet customer demand, controlling production quantity and product types over a fixed period of time.
Batch production is risky and inefficient, but while market demands are varying and the product demand is complex, Heijunka helps navigating your production planning to create flow.
If the demand over a certain time period averages to 100 units, the production will produce at this rate, but ahead of time at first to meet the daily demands within the time period.
To level based on types, the production will sequence the production with a combination of product types and not product complete batches of one type at the time. This includes risk and reduce agility.
To be able to implement Heijunka, it’s imperative to know the takt times of the production in order to schedule accordingly.
Heijunka box is a simple visualization of production planning using kanban.
Hoshin Kanri is a tool to ensure goal achievement according to your company’s strategies. Essentially a strategy implementation tool.
The tools are typically visualized using a hoshin matrix (x-matrix) diagram.
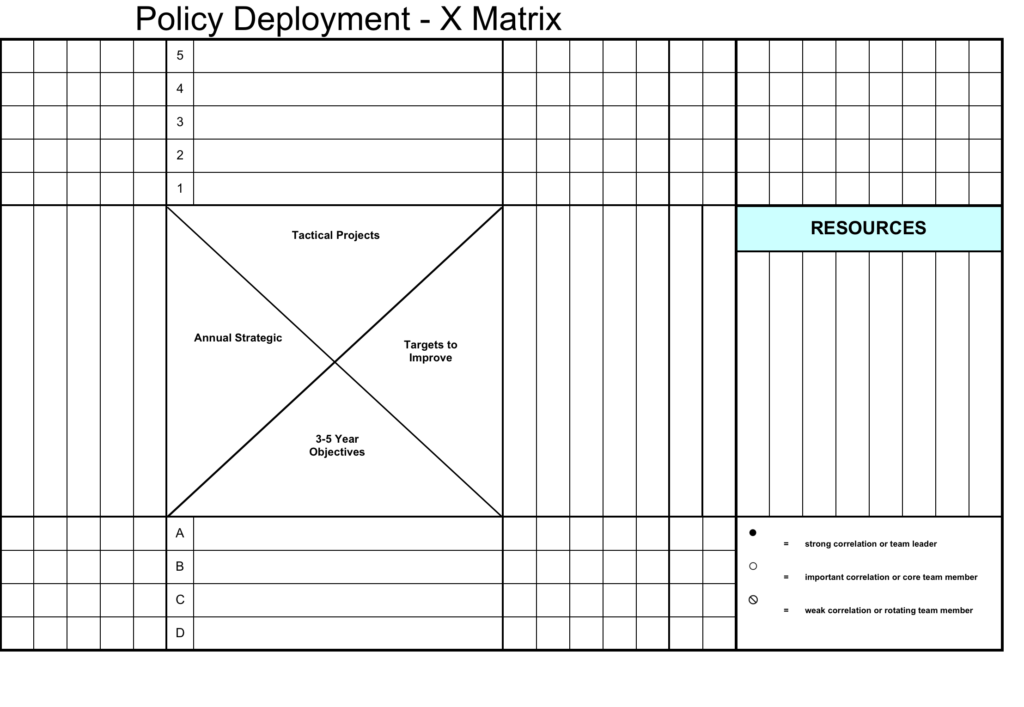
Hoshin Kanri can be used on all levels in the organization, breaking down top level strategies into goals for each division and departments. Using this method, ensure that all activities are priorities and vectored against goals that build upon the business strategies.
Translates to autonomization.
Autonomization implies automation with human intelligence.
The concept is to add intelligence to the machines and automation to differentiate bad from good products and act thereafter (Andon).
With Jidoka the company achieves greater autonomy and efficiency as the employees can manage multiple production lines simultaneously.
Toyota’s Just-In-Time (JIT) means making only what is needed, when it is needed and in the quantity that it demanded.
This principle does not only relate to the end product, but all parts of the production and value chain.
Many lean tools and principles build upon, and culminates to JIT. Creating flow using kanban is one of the most apparent ones, but also level production, eliminate waste, bottlenecks, inconsistencies etc.
Translates to radical change.
This Toyota philosophy focus on radical changes as means to improve production. Opposed to Kaizen, improvements that require more significant changes like new work methods, processes or new tools.
The results of Kaikaku are typically more eminent, but so are the risks.
Often referred to as continuous improvement. It’s a mindset, philosophy and attitude of an organization to continuously work with incremental improvements.
Kaizen should be used with the customer in focus. It means the organization will be agile and constantly subject to changes, adapting for the better in a low-risk, manageable way.
If integrated with Hoshin Kanri (Hoshin planning), improvements and activities will benefit customers at the same time it helps your organization reach its breakthrough goals for the strategic objectives.
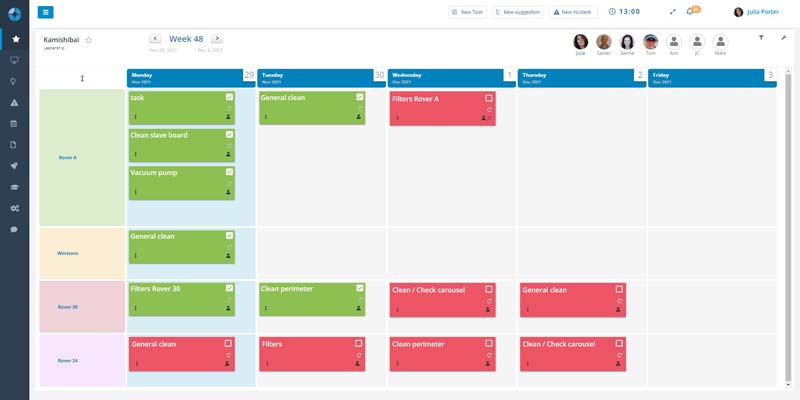
A kamishibai board is used to visualize and simplify audits or gemba walks in a production facility. The board consist of multiple cards or standard, planned activities to be performed. By default, they are red (to do) and you turn them around green when they are done. By having the board near the workplace, it’s easy to know what to do, how to do it, why do it, and it’s easy to see what is done and not.
Kanban is a system or method or even tool for scheduling and visualizing activities in a team or project. As part of the JIT philosophy, kanban focuses one item at the time (pull) to create flow.
Kanban boards are used to visualize the activities. This adds transparency within teams and proves to be effective on planning day-to-day activities.
Translates to death from overwork.
Karoshi is an occupational health issue and something to be aware of in the path to supreme effectiveness and competitive edge. There are many cases around the world where extensive overtime and overwork ends up in fatal health issues.
Key Performance Indicator. A defined goal metric to help indicate if you are on the right track or not.
Some KPIs may be quantified with set goals, and some may qualitative, indicated with a traffic light (green, yellow and red) indicating the status, risk or need for immediate action.
A quantitative measure for the process time.
For example, the time from order is placed to the product delivered.
Leader Standard Work (LSW) is a way to streamline the workday for managers and leaders. This happens through standardization of the activities.
Muda is one of the 3Ms developed by Toyota.
Toyota’s original 7 wastes of lean that consist of the defined wastes:
Later on, the western world adapted muda but added skills as the 8th waste; thus 8 wastes was established as its own term.
Mura is one of the 3Ms developed by Toyota.
Mura waste comes from unevenness or inconsistency in either production or customer demand.
Muri is one of the 3Ms developed by Toyota.
Muri is causing unnecessary stress and overburden to workers and processes. Mura can be one of the causes if the workload is inconsistent.
Smooth production flow, ideally one piece at a time, characterized by synchronization (balancing) of production processes and maximum utilization of available time, including overlapping of operations where practical.
Nemawashi is part of a decision-making process where information about forthcoming decisions are shared in order to build consensus. Employees are involved in the process and given their voice of opinion.
This process if considered informal to create the foundation for the decision process or project.
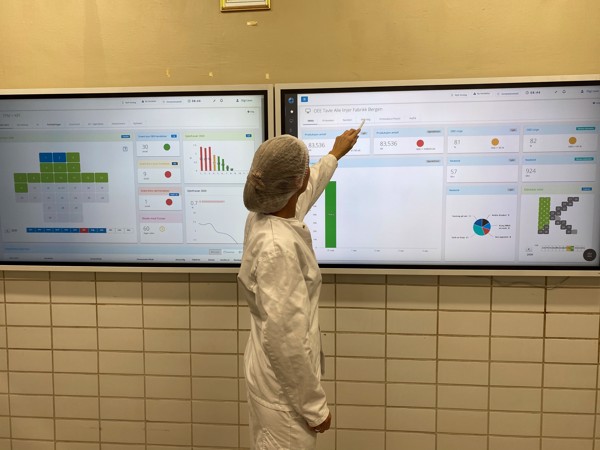
Sometimes referred to as Was Room or Control Room, Obeya is a concept to visualize an overview of different aspects of the operations.
The idea is to help teams manage daily challenges and performance with an eye on KPIs, strategy, problem-solving and other critical focus areas, all on one place.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness is a standard for measuring machine true production time, measure in %.
The overall OEE is calculated from three metrics; Availability, performance and quality.
The three metrics can be measured and visualized individually to understand the results of the overall OEE.
Translates to mistake-proofing. In contrast to baka-toke, poka-yoke focus on mistakes in process or action.
Plan, Do, Check, Act is a method used in continuous improvement to really ensure goals are achieved as planned.
It’s not uncommon that goals are set, actions are planned and executed, but never really evaluated or measured against the set goal.
PDCA is used to learn, reflect, investigate and understand, and lastly enable workers and management to correct their actions to really reach their goals.
One of the purposes with the PDCA cycle is to strive for perfection, always raise the bar, increase your standard and create sustainable improvements.
It is also one of the core principles of lean.
Root Cause Analysis.
Drill down to really understand a problem’s underlying causes. Fixing anything above the root cause is merely defined as a workaround.
There are many tools and methods to use for root cause analyses:
Pareto charts give you insight of problem types, areas and impact, so you know there the pain is.
Fishbone diagrams help brainstorm, analyze and visualize problems and causes.
5x why’s is a method to force participants to dive deeper into the problem and understand causes.
These can be used together or individually.
Related to manufacturing, this is a concept of having a flexible staff. This flexibility is used to accommodate variations in customer demands. Reading this can make you think it’s about having weak employee contracts, part-time employees or consultants to hire when needed, but IT’S NOT.
The concept is about training your employees to a broader range of the company’s operations. This way, the workers can be moved around and used for different tasks at the time when the workload is changed due to customer demand. The employees are trained to have multiple skills and an attitude to accept change and a dynamic work situation.
Six Sigma (6σ) is an American quality improvement principle developed by Bill Smith at Motorola in 1986. The concept is focusing on quality control through data and statistics. A Six Sigma state of a product production is defined as less than 3,4 defects per million opportunities.
Six Sigma does not fall directly under the Japanese lean umbrella, but can be seen a concept with tools and methods that are similar or can compare with traditional lean.
Both work against the same goal – to optimize efficiency and eliminate waste.
SMART is an acronym, helping to define your goals properly.
Smart goals are:
Specific
Measurable
Achievable
Reasonable
Time-bound
To achieve Kaizen and drive continuous improvement, you need to know what to improve. Your baseline is standardized work. It defines your current state, your work processes or methods that found the basis for your current work processes.
This should also be the baseline for improvements and where improvements are documented. Through Kaizen, your standards are revised and increased to a higher level of efficiency.
A measurement of your production flow according to the demand. Tact time is a figure telling you how long time you can spend on one unit to meet the customer demand for a production period.

Value Stream Mapping, perhaps one of the most typical lean tools, especially for organizations new to lean. VSM is used to map the current work processes visually using a large surface, sometimes on paper, across all the walls in a meeting room.
The purpose is to identify parts of the current processes that do not add value to the customers. By doing a VSM, you map out problem areas and improvement areas to address in the continued lean travel.
Foster24, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
A picture says more than a thousand words. Visual management is about communication, and visualization is far more effective communication than text.
Communicating status and tasks using graphic, intuitive elements using colors and symbols enable us to understand the purpose in a split second, just by a glance, rather than spending seconds or minutes reading a report.
Example:
Traffic light status
Red indicates a problem/stop
Amber indicates a warning. Precaution is required.
Green indicates all good, no need for action.

Yokoten is sharing of learning horizontally across your organization.
Expand your Kaizen laterally and improve the organization as a whole instead of sub-optimizing only one area or department.
Senior management is key to achieve Yokoten. They are the ones that have to facilitate the sharing culture and to make the cross-division assessment of learning.
Yokoten can also be practiced across your value chain including partners and suppliers, sharing learning between organizations where they collaborate, trade or interact.